Aim of the study
To design, develop and pilot test an interactive, tailored, internet and mobile enabled digital health intervention to enhance self-management of MetS among individuals living in urban poor settings.
Objectives of the Study
Objective 1
Objective 2
Objective 3
Mixed methods(Qualitative and quantitative research method)
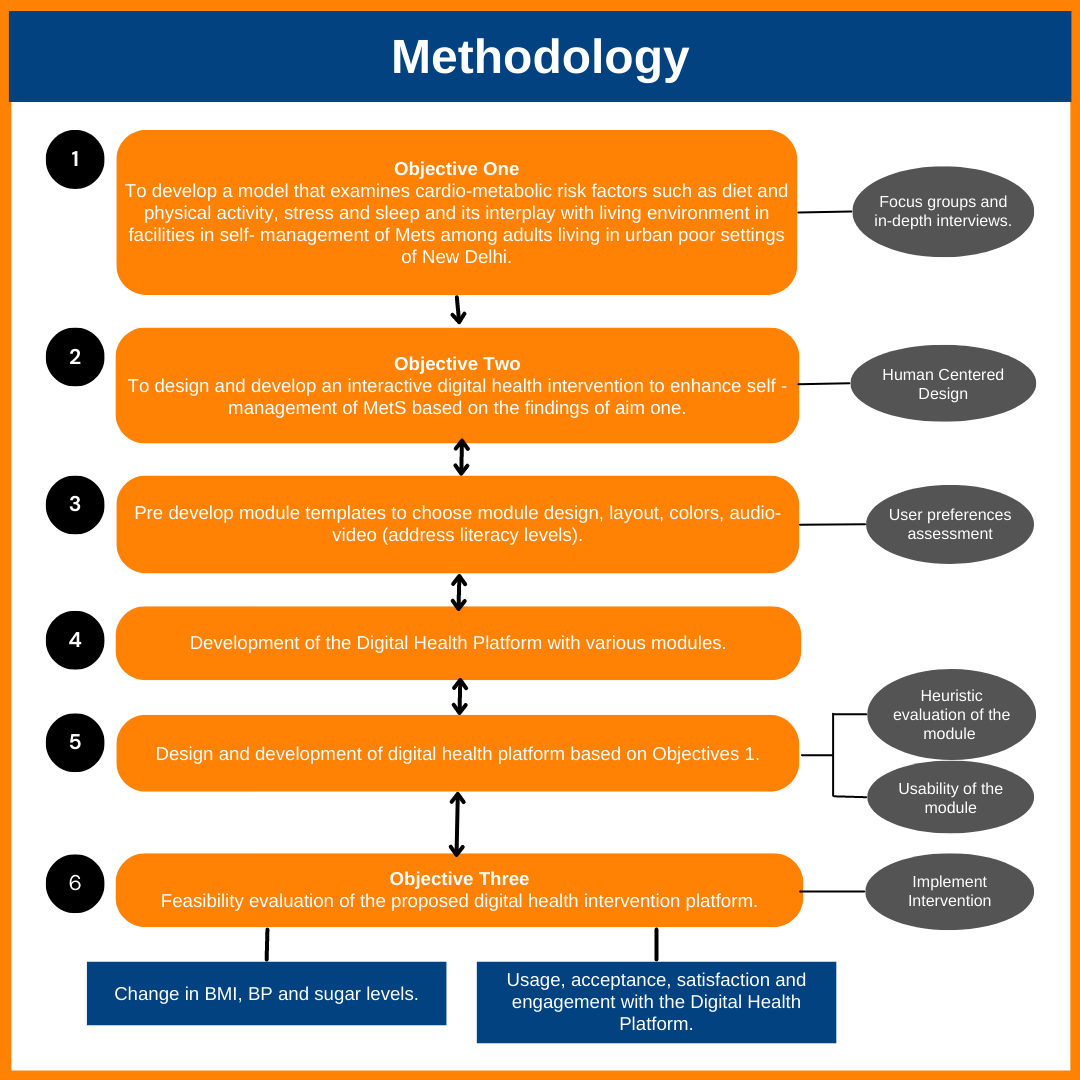
To achieve objective one, a mixed-method approach combining qualitative and quantitative assessments will be utilised to create a model that describes the interaction between the living environment and other cardio-metabolic risk variables such as nutrition, physical activity, stress, and sleep. The focus group talks and in-depth interviews will take place among a sample population of 120 participants drawn from distinct urban slum settings in four zones of New Delhi.
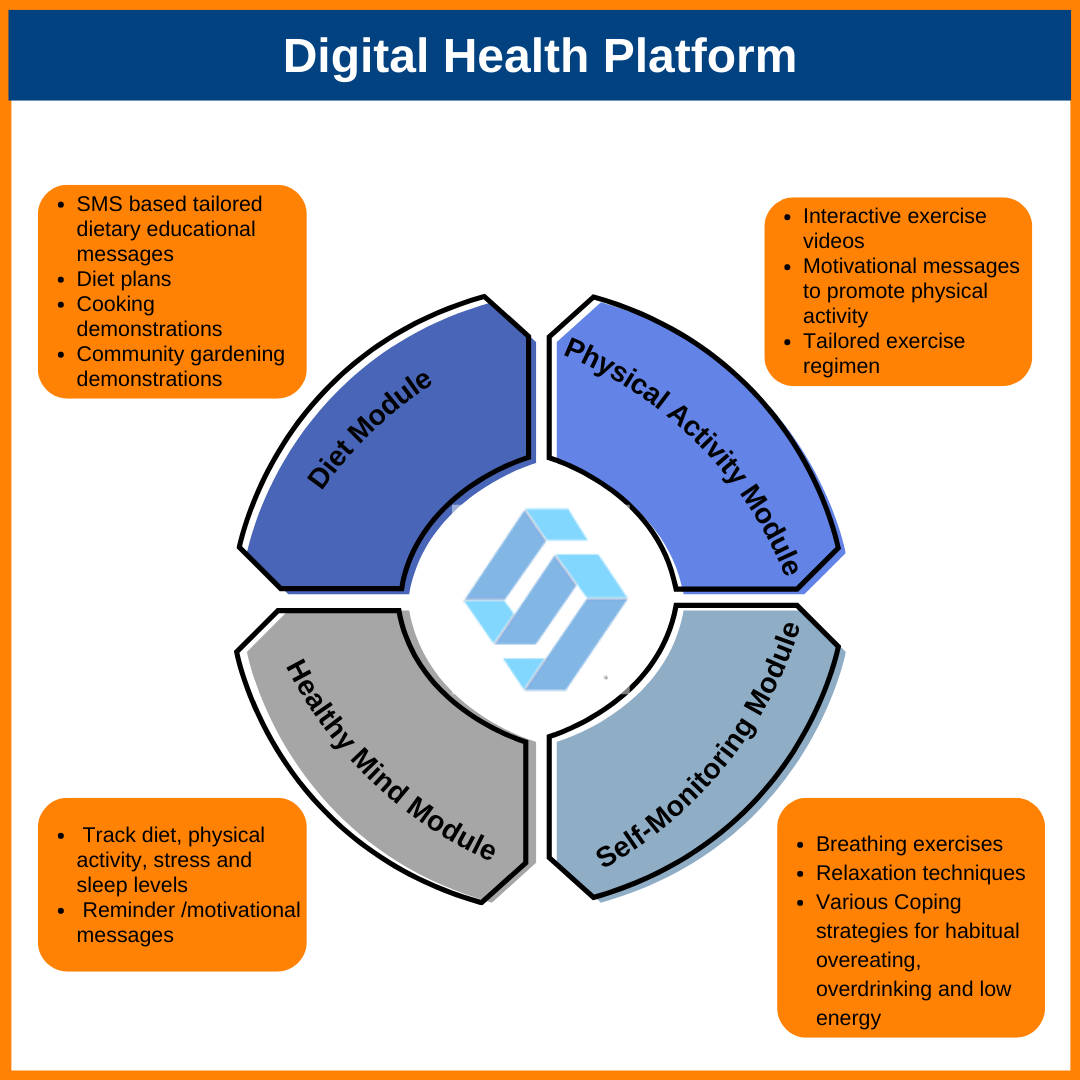
To achieve objective two, a quasi-experimental study design will be used in a sample of 80 participants, with a human-centered approach to design and develop an interactive, tailored mobile and internet-enabled digital health intervention platform aimed at supporting self- management among individuals living with MetS in urban poor settings. The findings of objective one will help in defining the essential elements/modules and features of the proposed digital health intervention platform.
A sample size of 30 people from each of the eight slums (240 participants) will be used to pilot test the utility and feasibility of the proposed digital health intervention in an urban poor community setting in New Delhi (areas including North, South, East, West, and Central zones of New Delhi) to measure usage, adherence, satisfaction, and acceptance with the proposed digital health intervention platform
West Zone
- Khazan Basti, Mayapuri
- Udyog Nagar, Peeragarhi
East Zone
- Ambedkar Camp, Kalyanpuri
- Indira Camp, Kalyanpuri
North Zone
- A Block, Shalimar Bagh
- Shaheed Udham Singh Park, Wazirpur Industrial Area
South Zone
- Kusumpur Pahari, Vasant Vihar
- Bhanwar Singh Camp, Vasant Vihar
- Objective 1 120 participants (15 participants from eight slums each)
- Objective 2 80 participants (10 paticipants from eight slums each)
- Objective 3 240 participants (30 participants from eight slums)

Dietary Diversity:The FAO’s Individual Dietary Diversity Score (IDDS) instrument will be used to examine diversity in individual participants’ diets. The tool comprises 16 food groups, nine of which will be analysed. Diets consisting of three food groups are classified as low diversity, diets consisting of four to five food groups are classified as moderate diversity, and diets consisting of more than six food groups are classified as high diversity.
“The Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Pathology Institutional Human Ethics Committee approved the study in January 2022, with approval number NIP-IEC/29-12-2021/05/01R1.The study will be carried out in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.”


